What is Hash and Hash Table
22 Jun 2020
Contents
- What is Hash Table ?
- Structure of Hash Table
- Basic Operations for Hash Table
- Collision Resolution
- Separate Chaining
- Open addressing
- Probe Sequence of Open Addressing
- Resizing
About Data Structure Hash Table
What is Hash Table ?
The Hash Table consists of key, value, hash function, hash, Bucket.
Hash Tableis a data structure that uses anassociative array structure.- Associative array
- An array in which one key and one data are paired 1:1.
- Value can be derived using the key.
- Associative array
KeysandValuesare paired.- Use
Hash functionto compute index(akaHash Code) using Key values into an array ofbuckets.
Structure of Hash Table
- Key : Key a unique value and input of hash function.
- Value : The value that is finally stored in a bucket and it must be paired with a key.
- Hash function : Compute the key to hash code.
- Hash or Hash code : The result of a hash function and stored in a bucket paired with a value.
- Bucket or Slot - Where the values are stored.
The key is computed to hash via hash function and the hash is matched with value and stored in the bucket.
Basic Operations for Hash Table
- Search - Search a value with a key.
- Insert - Compute key to hash through hash function and insert data.
- Delete - Delete a hash and value that matches a key.
But, there is a problem with Hash function.
Probelm with Hash Function
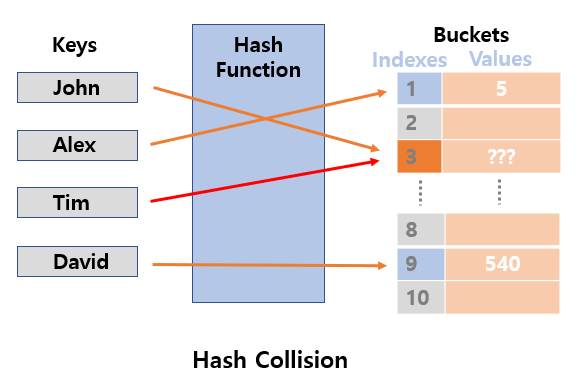
- Hash Collision : When different keys become the same hash code through a hash function, it is called
Hash Collision. - Overflow : If hash collisions occur more than the number of slots allocated to buckets, no more values can be inserted in buckets.
- Clustering : When data is concentrated in one record, it is called clustering.
In some cases, the value of all buckets may have to be looked up due to Hash Collision.
So, Time Complexity of Search, Insertion, and Delete => Best Case : O(1), Worst Case : O(N)
Therefore, it is important to create a function that reduces the probability of a hash collision as much as possible.
Collision Resolution
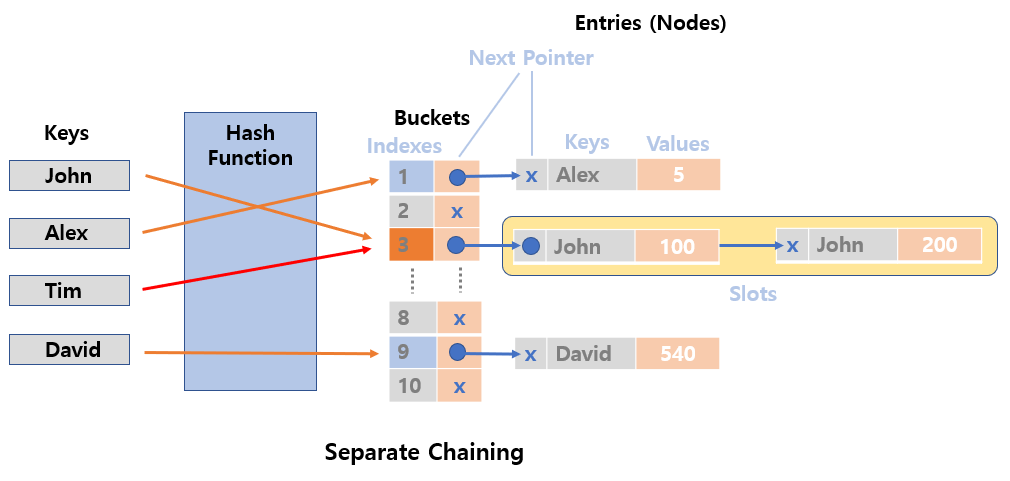
Separate Chaining
- In the separate chaining, each bucket is independent.
- Each bucket has some sort of list of entries with the
same index. - Use
linked listdata structure. - When a collision occurs in a bucket, it
links new datanext to theexisting data.
Change of Operations
Search
- Find the index through a hash function.
- Linearly check the list of connections in the corresponding index to see if the node of the key exists and return the value.
Insertion
- Insert a node to the linked list indicated by an index mapped with a key, and add a value to that node.
Deletion
- Linearly check the linked list of the corresponding index, delete the node of the corresponding key.
Advantage of Separate Chaining
- Limited bucket can be used efficiently.
- Use less memory because there is no need to allocate space in advance.
- The use of linekd list reduces the constraints of data that can be added.
Disadvantage of Separate Chaining
- Search efficiency is reduced when various keys have the same hash and one bucket has multiple entries.
- Requires additional memory to use linked list.
- Worst case of Separate chaining is
all nodes are inserted into the same bucket.
It is better to use Chaining when it is unknown how many and frequently keys many be inserted or deleted.
Open addressing
- Open addressing is a method that finds empty bucket and stores data.
- Hash table are maintained in a form where one hash and one value are matched.
- When a collision occurs in a bucket, the
index(hash)is changed to store it in another bucket.
Change of Operations
Deletion
- If we just delete a key, then search may not be worked.
- To prevent this, insert a
Dummy node(deleted)in the deleted location. So, it is possible toconnect to the next indexwhen searching. - If the number of dummy nodes increases,
rehashingis required to avoid performance reduction.
Advantage of Open Addressing
- Because no additional storage is needed, no additional work is required.
- By not using a pointer,
serializationis easy.
Disadvantage of Open Addressing
- The performance of a hash table depends on the performance of a hash function.
- The number of stored nodes cannot exceed the number of slots in the bucket array.
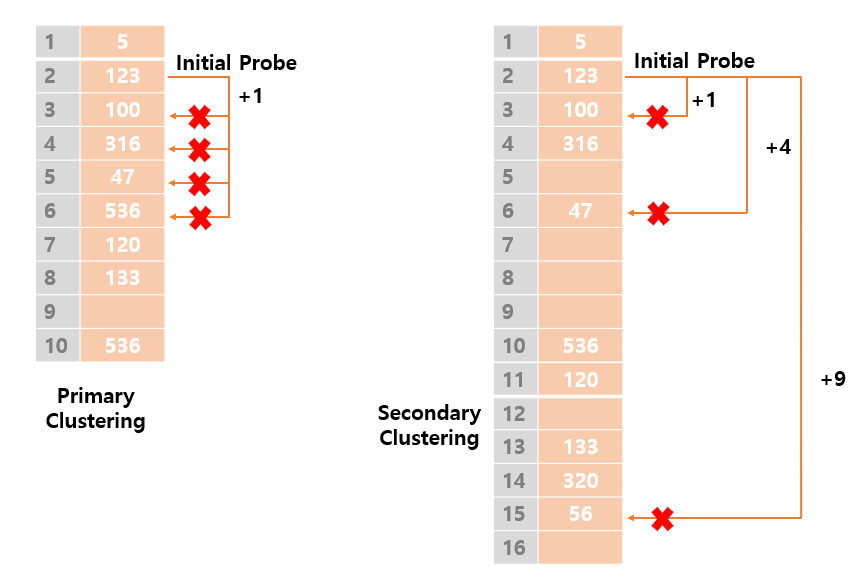
Probe Sequence of Open Addressing
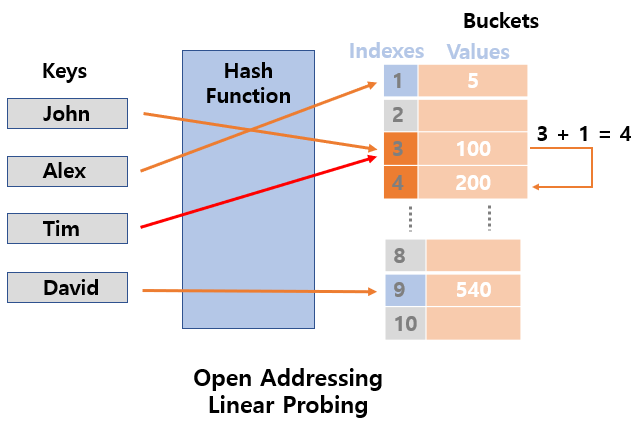
1. Linear Probing
- Linear Probing stores keys in the first empty bucket by
searching the empty space linearlyaccording to specific interval (usually 1) from the original index to.- hash + 1
- When you reach the end of the table, go back to the beginning of the table.
- Good CPU cache utilization
- However, in the worst case, it is inefficient and most vulnerable to
clustering of databecause it may require searching the entire hash table.
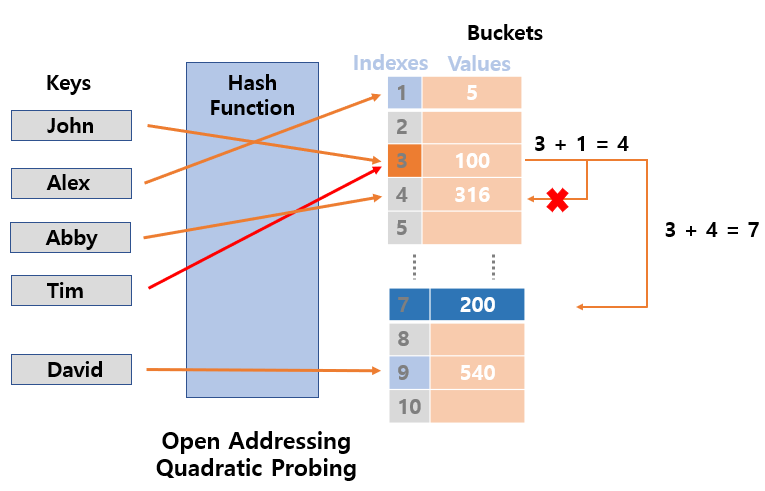
2. Quadratic Probing
- Primary clustering of linear probing can be solved, but
secondary clusteringcan occur. - Probe is calculated by adding
ouptut of a quadratic poly nomialto the original index. - Quadratic probing stores keys in the first empty bucket by searching empty space as far as
i^2from original index.- hash + 1, hash + 2, hash + 9
What is Primary Clusting and Secondary Clusting
-
Primary Clusting: After a hash collision, two of the keys in the hash table is hashed to the same position, and one of the keys is moved to the next position. Once this happens, the newly added keys also have the chance of experiencing another hash collision, even though the hash values are different.
- Primary Clusting causes
searching time of keywithin the cluster to be longer. - Especially
linear probing
- Primary Clusting causes
-
Secondary Clusting: Secondary clusting is occured when a low-quality hash function computes keys to same hash, then they will follow the same probe sequence or be placed in the same hash chain.
- Especially
linear probingandquadratic probing
- Especially
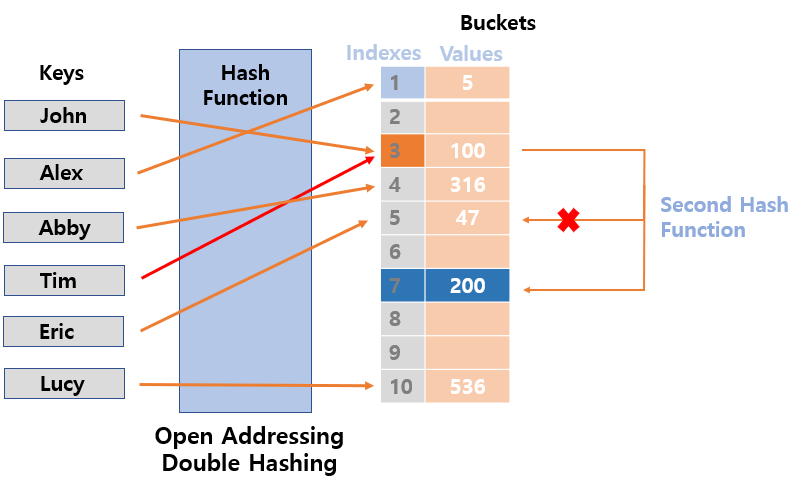
3. Double Probing
- Probe is calculated by a
second fash functionwhen a hash collision occurs. - The efficiency of CPU cach utilization is reduced but has little impact on clustering.
- However, more computation is required.
It is better to use Open Addressing when it is known how many and frequently keys many be inserted or deleted.
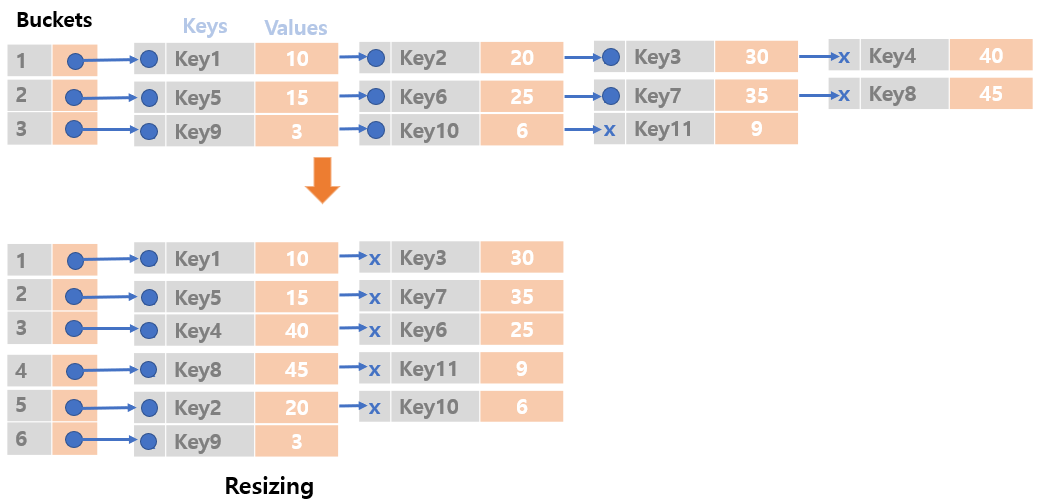
Resizing
- If the number of entries in a hash table exceeds the current capacity, then the hash table have to be rehashed.
- Rehashing means increasing the size of data structure and mapping existing datas to new bucket locations.
- Resizing
- In Separate Chaining, increase the number of buckets.
- In Open Addressing, increase the size of fixed-size arrays.
Implementation
Chaining Hash Table GitHub